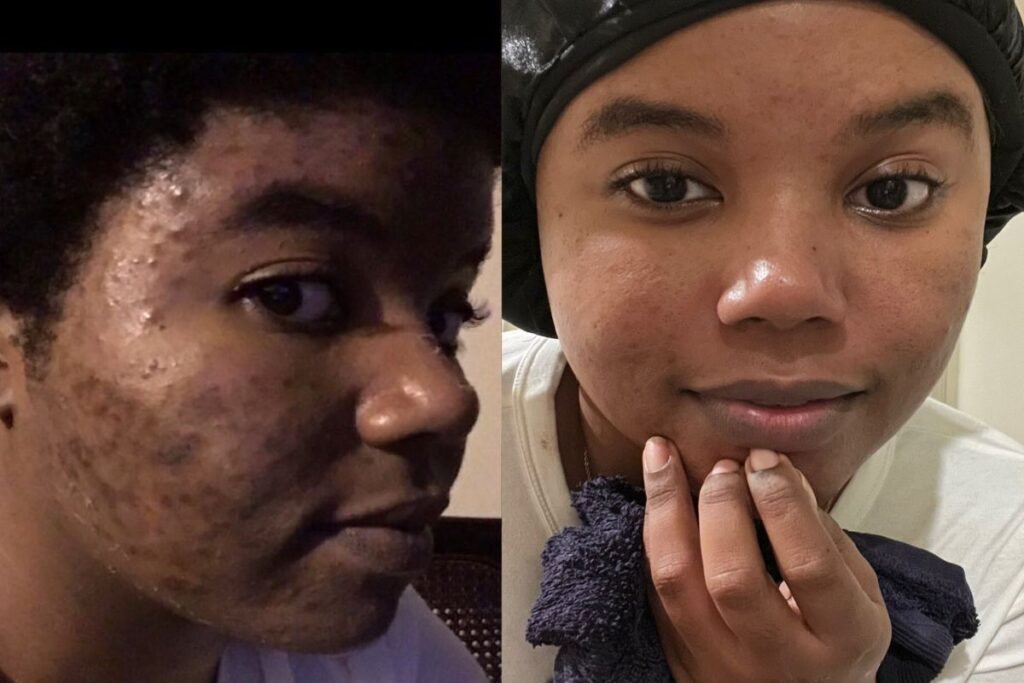
If you’ve noticed some strange color patches on your skin, you are most likely dealing with melasma or hyperpigmentation. Thankfully, dermatologists have released information on how to treat these skin attacks.
If not treated on time, these two skin conditions can keep you indoors against your wish, rob you of fun, and reduce your confidence. But you are not alone. In the United States, over 5 million people have these skin disorders.
In some cases, these skin challenges can die out on their own or with age. But in others, they can stay for a much longer time and require treatment before they can leave.
Read on to learn what solutions skin doctors recommend for these uneven skin tones. Equally important, we will examine the causes and differences between melasma and hyperpigmentation so you can tell one from the other.
ALSO READ: 15-Year-Old Heman Bekele Creates Soap That Could Prevent and Treat Skin Cancer
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a skin condition that results in the development of darker patches. It happens when the skin produces more melanin than is required.
Research has shown that skin of color is especially vulnerable to hyperpigmentation. That’s because darker skin tones already possess higher melanin levels. Also, while men can experience the condition, women have higher chances of suffering from it.
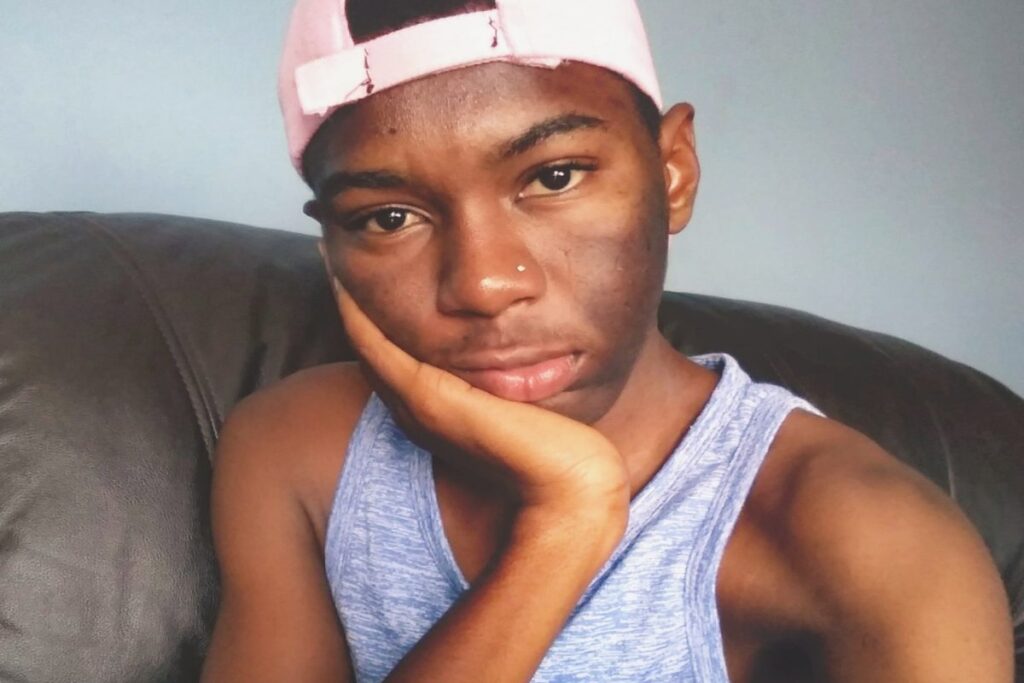

Hyperpigmentation can either manifest on the skin in a localized or diffused fashion. The localized appearance is smaller but more concentrated patches, while the diffused appearance is larger and less concentrated.
The localized hyperpigmentation is the more common one. It occurs as a result of inflammation or injuries to the skin, such as acne, hormonal imbalance from birth control or pregnancy, and UV damage.
There are three main types of hyperpigmentation. These are melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), and age spots. Dr. Teo Wan gave some insight into the differences between the three.
“Melasma quite classically presents as pigmented patches in a butterfly pattern on the cheeks and forehead. PIH tends to have fuzzy borders, whereas age spots have a discrete edge,” he explained.
What is Melasma?
Melasma, also known as “chloasma” or “black spot,” is a common skin disorder. It is a type of hyperpigmentation that causes blue-gray, light brown, or dark brown patches on the skin. These patches could produce flat or freckle-like spots on the skin.
“Melasma is a common acquired disorder of hyperpigmentation that affects sun-exposed areas,” says Dr. Murphy-Rose. “It appears as hyperpigmented, irregular patches and most commonly affects women of reproductive age and only rarely occurs in males. It has been linked to sun exposure and estrogen,” she further explained.
Melasma mostly affects parts of the face, such as the cheeks, the bridge of the nose, the chin, the forehead, and the upper lips. The skin condition also manifests on the forearms, neck, and shoulder. Besides reducing one’s attractiveness and, in some cases, self-esteem, it is a pretty harmless disorder.
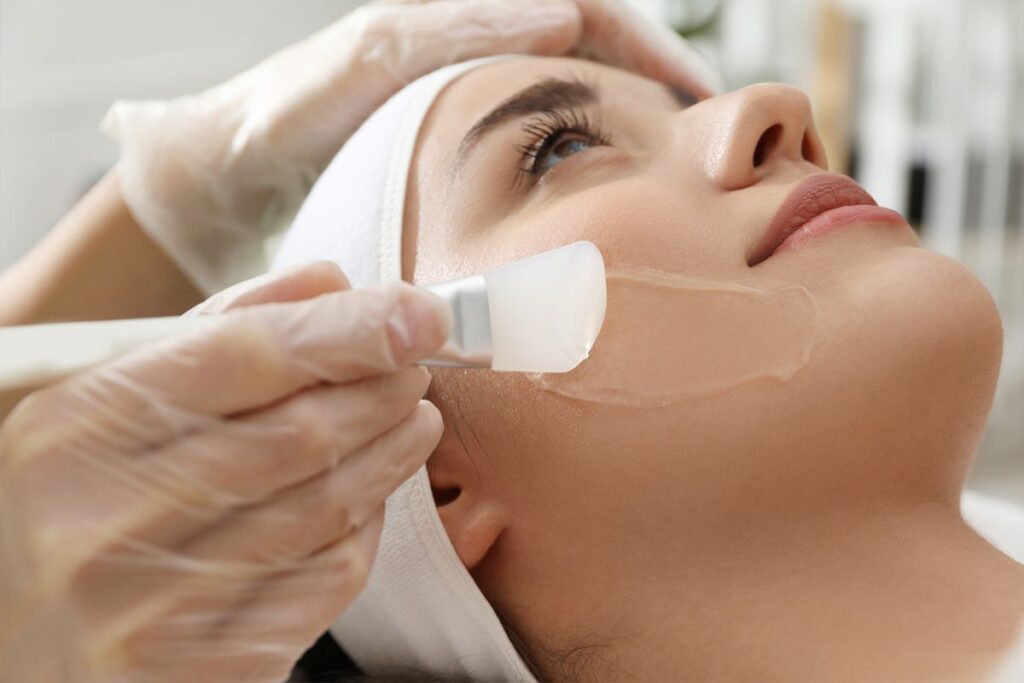
What is the Main Cause of Melasma?
Doctors are still not completely sure why melasma occurs. Some experts believe that they could result from the malfunction of the color-making cells in the skin called melanocytes. What is certain, however, is that these cells release too much melanin. This excess melanin then produces spots on the skin.
According to the American Board of Dermatology, melasma commonly occurs during a woman’s reproductive years. Females, especially pregnant ones, are at greater risk of the disorder. The board also revealed that only 10% of melasma cases are in males.
Risk factors that result in melasma include frequent exposure to UV rays from the sun and light brown skin tones. Others are pregnancy and female sex. Females are nine times more prone to melasma than males.
In addition, genetics plays a role in exposing one to the disorder. Studies have shown that about half of the people with melasma have close relatives with the condition.
ALSO READ: How to Use Retinol on Your Skin For Better Results
What is the Best Cure for Melasma?
According to skin experts, calling the attention of a certified dermatologist is the first step to take in getting rid of melasma. “If the problem is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation — acne, a superficial scrape — then it may be reasonable to try at-home remedies, such as the MadisonMD Skin Care Uneven Pigment Fighter, for a month or two,” says seasoned dermatologist, Dr. Brandith Irwin.
Irwin also advised that although resurfacing treatments like lasers are pretty effective for other types of hyperpigmentation, they aren’t so for melasma. They could worsen the condition. For the best cure for melasma, physicians recommend dermatological procedures such as chemical peels, light therapy, dermabrasion, and microdermabrasion.
Doctors also trust hydroquinone to treat melasma. Hydroquinone is available as a lotion, cream, or gel. Simply apply it to the patches of discolored skin. Corticosteroids and tretinoin also help lighten the color of the darker skin patches.

What’s the Difference Between Melasma and Hyperpigmentation?
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation. Thus, they have a number of things in common. However, there are differences—ways you can distinguish one from the other. First, while melasma is mainly caused by hormonal changes, hyperpigmentation commonly results from sun exposure, skin injuries, acne scars, and inflammation.
Secondly, melasma appears as symmetrical patches with distinct borders, while hyperpigmentation appears as isolated spots and uneven patches.
Does Melasma Come Back After Stopping Hydroquinone?
Melasma and other types of hyperpigmentation can resurface after using hydroquinone. Hydroquinone combats melasma by reducing the number of melanocytes and hindering their melanin production.
On continuous exposure to the sun’s UV rays, melasma can return after using hydroquinone. One popular dermatologist tips concerning hydroquinone is that an affected person maintains the result by protecting themselves from the sun.
Experts recommend the daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen. Also, sun-protective covering such as brimmed hats will prove useful.
You Might Also Like:
Arizona Man Chris Zwierzynski Survives a 700-Foot Fall on Oregon’s Mount Hood
15-Year-Old Heman Bekele Creates Soap That Could Prevent and Treat Skin Cancer
Man Recounts Surviving a Black Bear Attack in California Foothills While on a Run
Lady Gaga Flaunts New Dark Hair Amid Collab Rumors With Bruno Mars
Former NFL Player Cierre Wood Sentenced for Murdering Five-Year-Old Because She Was “Chunky”